How to Get the Best Email Deliverability
Don't Send Emails through a Shared IP Address
Deliverability and reputation problems can occur if you are using a shared IP address to send out your emails while other senders use the same IP address. If the other senders emails get marked as spam or the shared IP address gets blacklisted your IP will be blacklisted and/or your emails will land in the junk folder. Many ESPs automatically use shared IP addresses across many clients.
Lead Liaison assigns a dedicated IP address to each customer. Trials are run using a shared IP address pool. Even in the pool, there are multiple IP addresses to prevent one from going down and affecting other trials.
Warm up your IP Address
If you're just starting out with Lead Liaison or your IP address has changed you will need to warm up your IP address to develop a reputation with the ISPs. If you suddenly send out 30,000 emails in one day from a new IP your messages will be limited or purposely throttled by ISPs. If you're in the thousands of emails to begin with you might avoid scrutiny. However, if bounces, spam complaints, or spam trap hits represent a high percentage of your emails sent you'll damage your reputation right out of the box. Make sure you initial sends are to very clean lists.
Use Caution with Old Database Contacts
Try not to send emails to invalid or very old contacts in your database. It's best to run some type of database cleansing tool on your database first. If you send a single message to your entire database and include these dormant contacts you could have a high percentage of bounces. Additionally, old email addresses could be spam traps. Bounces and spam traps will send a notification to the ISP and damage your reputation. The best practice is to send frequent emails to small amounts of old contacts, vs. sending to your entire database or all old contacts, and monitor results. If you're getting lots of bounces phase out this effort. Conduct this "experiment" only after establishing a good reputation.
Use Authentication
As discussed, establishing a good reputation is vital for email deliverability. To protect your reputation several methods have been developed by various consortiums. These methods verify your email messages come from an authorized server and not from a nefarious source. The solutions are DomainKeys/DKIM and Sender ID/SPF records. Each authentication method is described below.
DomainKeys/DKIM
Created by Yahoo!, DomainKeys/DKIM is an authentication scheme that signs messages based on the "from" header and a DNS (Domain Name Server) record maintained by your DNS servers. For example, if your company's domain name is registered with GoDaddy.com there's a good chance your DNS is also hosted with GoDaddy.com. To keep it simple, a DNS is a set of rules and parameters for your domain name. Since your DNS is managed by you and hosted inside a secure area (such as GoDaddy.com) it's a secure way to prove the "from" address originated from the correct mail servers.
DomainKeys/DKIM validates emails using two security keys. The keys encrypt messages before delivery and validate the message at delivery time. DKIM and DomainKeys are very similar; however, DKIM was created by several companies to enhance DomainKeys. Today, major ISPs such as Google (@gmail.com) and Yahoo! (@yahoo.com) use DKIM.
Benefits of using DomainKeys/DKIM:
- It allows the originating domain of an e-mail to be positively identified, allowing domain-based blacklists and white lists to be more effective. This is also likely to make phishing attacks easier to detect.
- It allows forged e-mail messages to be discarded on sight, either by end-user e-mail software (mail user agents), or by ISPs' mail transfer agents.
- It allows abusive domain owners to be tracked more easily.
- It allows a great reduction in abuse desk work for DKIM-enabled domains if e-mail receivers use the DKIM system to automatically drop forged e-mail messages claiming to be from that domain.
- The domain owner can then focus their abuse team energies on their own users who actually are abusing their use of that domain.
Lead Liaison uses a premier email marketing engine from Port25 which enables authentication using DomainKeys/DKIM. Lead Liaison will completely configure DomainKeys/DKIM for you. No setup is required on your part. Your Lead Liaison Revenue Success Manager will set this up.
Sender ID/SPF
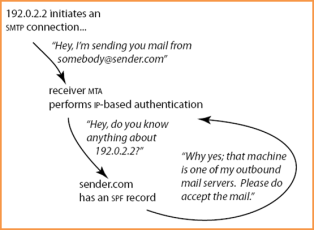
Sender ID/SPF prevents other people/servers from pretending to be you. Sender Policy Framework (SPF) is similar to DomainKeys/DKIM since it validates you as the sender; however, the implementation is different from DomainKeys/DKIM. SPF works by publishing what is called a "reverse MX" record to tell the internet what machines are allowed to send mail from the domain.
Sender ID and SPF are different. Both validate email sender addresses using similar methods, publish records in DNS and use the same syntax for their policy records. They are different in what they validate and the layer of the email system they check.
Sender ID and SPF is configured outside of Lead Liaison and should be done by your company. The setup requires changing your DNS record. You can check where your DNS is hosted here: http://whois.domaintools.com/http://whois.domaintools.com/ and possibly enlist support from your DNS host to help you change the record.
There are wizard's to help configure SPF and Sender ID available here:
- SPF: http://www.openspf.org/http://www.openspf.org/
- Sender ID: http://www.microsoft.com/mscorp/safety/content/technologies/senderid/wizard/http://www.microsoft.com/mscorp/safety/content/technologies/senderid/wizard/
Here are a few simple rules to keep in mind when configuring your Sender ID / SPF record to work with Lead Liaison:
- If you already have your own SPF or Sender ID record set up, all you need to do is add "include: leadliaisonconnector.com" to the existing record and you're done.
- SPF clients ignore records which do not carry a recognized version such as "v=spf1".
- A domain MUST NOT return multiple records that begin with the version "v=spf1". If more than one "v=spf1" record is returned, this constitutes a syntax error and the result is "unknown".
List of ISPs and the Authentication Methods they use
ISP |
Authentication type |
AOL (aol.com) |
SPF/Sender-ID//DKIM |
CompuServe (compuserve.com) |
SPF/Sender-ID/ |
Netscape (netscape.com) |
SPF/Sender-ID/ |
Bellsouth (bellsouth.net) |
SPF |
Charter (charter.net) |
SPF |
Comcast (comcast.net) |
SPF |
Cox (cox.net) |
DKIM |
Earthlink (earthlink.net, mindspring.com, peoplepc.com) |
DomainKeys |
Google(gmail.com) |
SPF/ DomainKeys /DKIM |
Juno/NetZero (juno.com, netzero.net) |
SPF/Sender-ID |
Microsoft (msn.com, hotmail.com) |
SPF/Sender-ID |
RoadRunner (rr.com) |
SPF |
Verizon (verizon.net) |
SPF |
Yahoo! (yahoo.com) |
DomainKeys |
SBCGlobal (sbcglobal.net) |
DomainKeys |
British Telecom (btinternet.com) |
DomainKeys |
Rogers Cable (rogers.com) |
DomainKeys |
Rocket Mail (rocketmail.com) |
DomainKeys |
Consider Using a Different Related Domain to Send Emails
If you're sending lots of email marketing messages from the same domain as your email addresses and these messages get marked as spam or land in the spam box you could affect other employees ability to send emails. If you are not careful with your email marketing practices lots of recipients might designate your email as spam and your corporations domain might get blacklisted. Then, no one will be able to send emails in your company. Consider using a different domain for your email marketing. Make it similar to your primary domain. For example, ourcompany.com could be our-company.com.
Use a 3rd Party ESP like Lead Liaison
Reputable ESPs provide many advantages. For example, they:
- are white listed with the ISPs
- are tied into feedback loops with ISPs (to receive notice of spam messages or blacklisting)
- have software programs to ensure messages are CAN-SPAM compliant
- have authentication procedures such as Domain Keys, DKIM, SenderID, and SPF
- can help you troubleshoot issues and avoid making mistakes
- keep up on the email marketing and email deliverability industry
Lead Liaison provides these six advantages with every software subscription license.
Manage your Reputation with the ISPs
ISP reputation is based on
- volume history,
- spam complaints,
- spam trap hits,
- bounce percentages,
- proper authentication and
- blacklist entries.
To build and maintain a good reputation
- require double opt-in,
- scrub your lists for bounces,
- do not buy, rent or borrow third-party lists,
- setup a postmaster and abuse email address for any complaints,
- monitor feedback loops,
- authenticate with DKIM/DomainKeys,
- authenticate with SenderID,
- authenticate with SPF, and
- do not mail to old or invalid database contacts.
Lead Liaison automatically appends an unsubscribe link to the bottom of email messages to provide recipients with the choice of opting out instead of hitting the spam button.
Handling Email Bounces
Email bounces are automatically processed by Lead Liaison. After processing your emails, subscribers will be marked appropriately, and you can access all bounce related statistics from the Statistics ? Email Campaign Stats or Statistics ? Contact List Stats pages. Hard bounces will mark a Subscriber as "Bounced" by the application after one bounce, and deal with problems like "email address doesn't exist" or "invalid domain name". Soft bounces take 5 times to remove a subscriber from your list, and deal with more common problems like "relay problem" or "mailbox is full".
Lead Liaison also has a process to configure DKIM/DomainKeys, SenderID and will support you when setting up your SPF record.
Resolve Spam Complaints
Occasionally recipients may report a complaint to an ISP. ISPs will look for a way to communicate with your company. It is recommended postmaster@yourdomain.com and abuse@yourdomain.com are set up as valid email accounts and go to someone that can and will actually do something about complaints.
Check Blacklist Records
Ensure your dedicated IP address is not listed on any RBL (real-time black lists). You can do this by checking http://www.mxtoolbox.com/SuperTool.aspxhttp://www.mxtoolbox.com/Su%3Cdiv%20class= http://www.mxtoolbox.com/Su%3Cdiv%20class=
[
http://www.mxtoolbox.com/Su%3Cdiv%20class=] [ |
http://www.mxtoolbox.com/Su%3Cdiv%20class=] |
perTool.aspx" class="external-link" rel="nofollow"linktype="raw" wikidestination="http://www.mxtoolbox.com/Su http://www.mxtoolbox.com/Su%3Cdiv%20class=[
http://www.mxtoolbox.com/Su%3Cdiv%20class=] perTool.aspx" originalalias="http://www.mxtoolbox.com/Su perTool.aspx" >http://www.mxtoolbox.com/Su perTool.aspx and typing in "blacklist: yourdedicatedipaddress" into the field. Lead Liaison will help you manage black list entries to keep your dedicated IP address in good standing with the ISPs. |
Monitor Feedback Loops
Each ISP sets up a feedback loop. A feedback loop is a way for recipients to directly communicate complaints with an ISP and allow the ISP to communicate the complaint to the offender. The feedback loop is used to monitor complaint rates and make sure you aren't hitting any spam traps. There are several feedback loops Lead Liaison will sign your IP address up for. Lead Liaison will monitor feedback loops on your behalf.
Follow the CAN-SPAM Act Requirements
Any companies not following CAN-SPAM compliancy will be in violation of their contract and subject to disengagement with Lead Liaison.
- Provide a way for your subscribers to opt-out of receiving future e-mails.
- Make sure your e-mail includes your physical address.
- Make sure the e-mail header information clearly identifies your business and does not mislead your audience in any way.
- Make sure your e-mail subject line isn't misleading.
- Make sure your e-mail clearly states that the e-mail is a solicitation unless you have permission.
- Make sure your e-mail complies with any applicable guidelines for sexually oriented material.
© 2021 Lead Liaison, LLC. All rights reserved.
13101 Preston Road Ste 110 – 159 Dallas, TX 75240 | T 888.895.3237 | F 630.566.8107 www.leadliaison.com | Privacy Policy